Now that we know what Linux is, it is the time that to learn how we should install it on the computer and choose which Distribution we should use. Let us start by understanding what a Linux Distribution is.
Sudo /path/to/unzippedrEFInd file/install.sh to install it. When you boot your Mac with the LiveUSB inserted, you should have the above options in rEFInd. Choose the one denoted above to access the Ubuntu installer. Step 1: Ubuntu Installation. Insert the LiveUSB you made earlier, and reboot your Mac. Installing Linux on a Mac. Yes, there is an option to run Linux temporarily on a Mac through the virtual box but if you’re looking for a permanent solution, you might want to completely replace the present operating system with a Linux distro. To install Linux on a Mac, you’ll need a formatted USB drive with storage up to 8GB.
In this tutorial, we will learn -
What is a Linux Distribution?
Well, now as you know that Linux is open-source, free to use kernel. It is used by programmers, organizations, profit and non-profit companies around the world to create Operating systems to suit their individual requirements.
To prevent hacking attempts, many organizations keep their Linux operating systems private.
Many others make their variations of Linux available publicly so the whole world can benefit at large.
These versions/ types /kinds of Linux operating system are called Distributions.
Linux For Mac
Click here if the video is not accessible
How many distributions are out there?
There are hundreds of Linux operating systems or Distributions available these days. Many of them are designed with a specific purpose in mind. For example, to run a web server or to run on network switches like routers, modems, etc.
The latest example of one of the most popular smartphone-based Linux Distribution is Android!
Many of these Distributions are built to offer excellent personal computing.
Here, are a few popular Linux Distributions (also called Linux Distro) -| Linux Distribution | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Arch | This Linux Distro is popular amongst Developers. It is an independently developed system. It is designed for users who go for a do-it-yourself approach. | |
| CentOS | It is one of the most used Linux Distribution for enterprise and web servers. It is a free enterprise class Operating system and is based heavily on Red Hat enterprise Distro. | |
| Debian | Debian is a stable and popular non-commercial Linux distribution. It is widely used as a desktop Linux Distro and is user-oriented. It strictly acts within the Linux protocols. | |
| Fedora | Another Linux kernel based Distro, Fedora is supported by the Fedora project, an endeavor by Red Hat. It is popular among desktop users. Its versions are known for their short life cycle. | |
| Gentoo | It is a source based Distribution which means that you need to configure the code on your system before you can install it. It is not for Linux beginners, but it is sure fun for experienced users. | |
| LinuxMint | It is one of the most popular Desktop Distributions available out there. It launched in 2006 and is now considered to be the fourth most used Operating system in the computing world. | |
| OpenSUSE | It is an easy to use and a good alternative to MS Windows. It can be easily set up and can also run on small computers with obsolete configurations. | |
| RedHat enterprise | Another popular enterprise based Linux Distribution is Red Hat Enterprise.It has evolved from Red Hat Linux which was discontinued in 2004. It is a commercial Distro and very popular among its clientele. | |
| Slackware | Slackware is one of the oldest Linux kernel based OS's. It is another easy desktop Distribution. It aims at being a 'Unix like' OS with minimal changes to its kernel. | |
| Ubuntu | This is the third most popular desktop operating system after Microsoft Windows and Apple Mac OS. It is based on the Debian Linux Distribution, and it is known as its desktop environment. |
The Best Linux Distribution!
The term best is relative. Each Linux distribution is built for a specific purpose-built to meet the demands of its target users.
The desktop Distributions are available for free on their respective websites. You might want to try them one by one till you get to know which Distribution you like the most. Each one of them offers its own unique design, applications, and security.
We will be using Ubuntu for our learning purpose as it's easy for a beginner to understand.
Installing Linux
Let's look the various methods we can use to install Ubuntu.
Installing Linux using USB stick
This is one of the easiest methods of installing Ubuntu or any distribution on your computer. Follow the steps.
Step 1) Download the .iso or the OS files on your computer from this link.
Step 2) download free, software like 'Universal USB installer to make a bootable USB stick.
Step 3) Select an Ubuntu Distribution form the dropdown to put on your USB
Select your Ubuntu iso file download in step 1.
Select the drive letter of USB to install Ubuntu and Press create button.
Step 4) Click YES to Install Ubuntu in USB.
Step 5) After everything has been installed and configured, a small window will appear Congratulations! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
Installing Linux using CD-ROM
Those who like the way a CD runs should try using this method.
(image source)
Step 1) Download the .iso or the OS files onto your computer from this link http://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop.
Step 2) Burn the files to a CD.
Step 3) Boot your computer from the optical drive and follow the instructions as they come.
Installing Linux using Virtual Machine
This is a popular method to install a Linux operating system. The virtual installation offers you the freedom of running Linux on an existing OS already installed on your computer. This means if you have Windows running, then you can just run Linux with a click of a button.
Virtual machine software like Oracle VM can install Ubuntu in easy steps. Let us look at them.

Here the brief steps
PART A) Download and Install Virtual Box
Download Virtual box using this link
Depending on your processor and OS, select the appropriate package. In our case, we have selected Windows with AMD
Once the download is complete, Open setup file and follow the steps below:
Step-1) Click On next
Step-2) Select you're the directory to install VirtualBox and click on next
Step-3) Select Desktop icon and click on next, now click on yes

Step-4) Click On install.
Step-5) Now installation of the virtual box will start. Once complete, click on Finish Button to start Virtual Box
The virtual box dashboard looks like this-
PART B) Download Ubuntu
Visit this link to download Ubuntu.
You can select 32/64-bit versions as per your choice.
PART C) Create a Machine in Virtual Box
Step-1) Open Virtual box and click on new button
Step-2) In next window, give the name of your OS which you are installing in virtual box. And select OS like Linux and version as Ubuntu 32 bit. And click on next
Step-3) Now Allocate Ram Size To your Virtual OS. I recommended keeping 1024mb (1 GB) ram to run Ubuntu better. And click on next.
Step-4) Now To run OS in virtual box we have to create virtual hard disk, click on create a virtual hard drive now and click on create button.
The virtual hard disk is where the OS installation files and data/applications you create/install in this Ubuntu machine will reside
Step-5) select VHD (virtual hard disk) option and click on next.
Step-6) Click on dynamic allocated and click on next. This means that the size of the disk will increase dynamically as per requirement.
Step-7) Allocate memory to your virtual hard drive .8GB recommended. Click on create button.
Step-8) Now you can see the machine name in left panel
So a Machine (PC) with 8GB Hardisk, 1GB RAM is ready.
PART D) Install Ubuntu on the Machine
Step 1) Select the Machine and Click on Start
Step 2) Select the Folder Option
Step 3) Select the Ubuntu iso file

Step 4) Click Start
Step-5) You have an option to Run Ubuntu WITHOUT installing. In this tutorial will install Ubuntu
Step-6) Click continue.
Step-7) Select option to erase the disk and install Ubuntu and click on install now. This option installs Ubuntu into our virtual hard drive which is we made earlier. It will not harm your PC or Windows installation
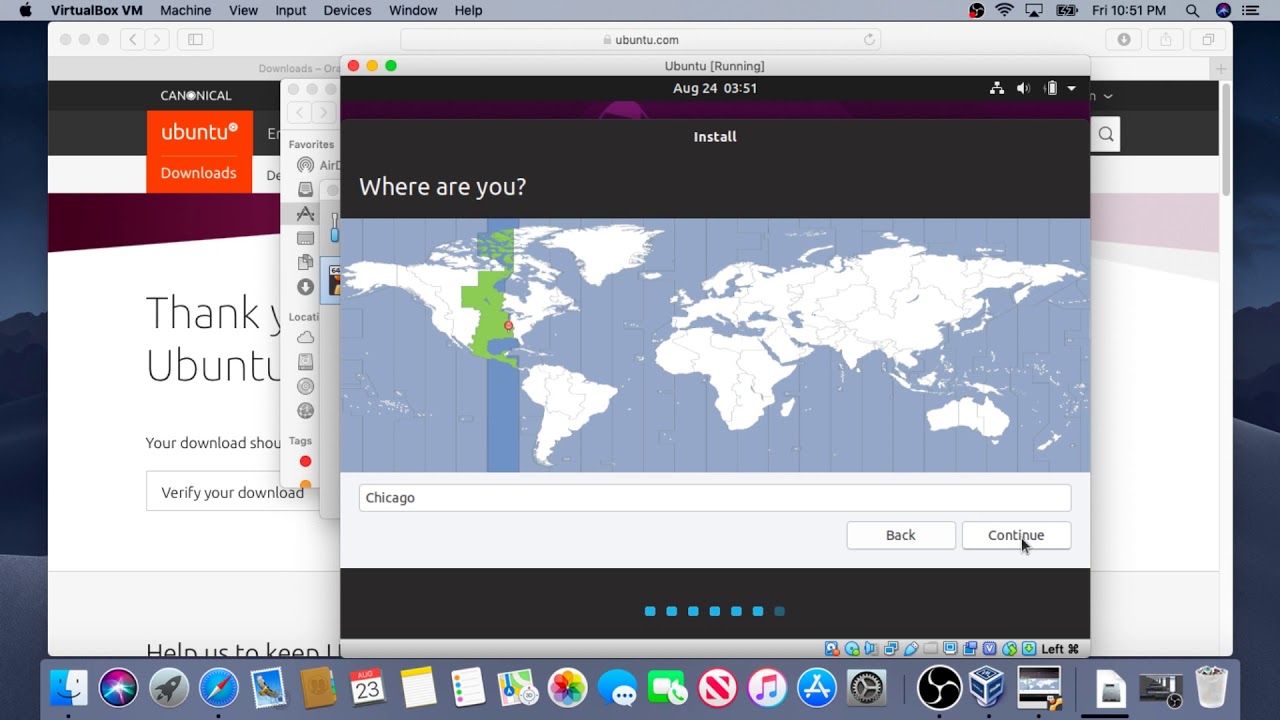
Step-8) Select your location for setting up time zone, and click on continue
Step-9) Select your keyboard layout, by default English (US) is selected but if you want to change then, you can select in the list. And click on continue
Step-10) Select your username and password for your Ubuntu admin account. This information has been needed for installing any software package into Ubuntu and also for login to your OS. Fill up your details and tick on login automatically to ignore login attempt and click on continue
Step-11) Installation process starts. May take up to 30 minutes. Please wait until installation process completes.
Step-12) After finishing the installation, you will see Ubuntu Desktop.
Summary
- An operating system based on the Linux kernel is called a Distribution or Distro
- There are hundreds of Distributions available, some of which are designed to accomplish a sole purpose like running servers, act as network switches, etc.
- Naming the best Linux Distribution is difficult as they are made for different.
- Linux can be installed on your system via the below-mentioned methods:
- USB stick
- Live CD
- Virtual Installation
More and more Linux operating system becomes popular especially for geeks, system administrators or developers. Several popular Linux operating systems for desktop are Ubuntu, LinuxMint and Elementary OS. This post will show you how to install LinuxMint 17.3 on MacBook Pro dual-boot with OS X El Capitan. This method should also be applicable for Ubuntu 15.10 and Elementary OS 0.3.2 Freya.

Prepare the partition
We can use Disk Utility to partition our disk. Create around 50GB of disk space for Linux. Set the partition format to MS-DOS(FAT). We can change to EXT4 Linux file system format later in the installation stage.
To make it easier, I have created a video how to partition the disk on OS X El Capitan.
Create Ubuntu / LinuxMint bootable USB Stick Installer for Macbook
We will install the Linux operating system using a USB stick. You need at least 4GB of USB stick. Ubuntu website already provides how to create a bootable USB stick on OS X on this page.
The steps is as follows:
To make it easier I have created a video on how to create Ubuntu / LinuxMint bootable USB stick on OS X
Restart the MacBook to boot on USB stick
After successfully create the bootable USB stick, it is time to boot the Macbook to USB stick. Press and hold Option key while booting to go to Mac boot menu. Select the EFI boot disk. If there are two EFI boot disks just select one of them. The Mac should boot into Linux running on USB stick.
Basically you can run the Ubuntu / LinuxMint / Elementary OS just from Linux. It is called Live USB Linux. You have to always and keep the USB plugged in to run Live USB Linux. If you wish to install it to hard disk, double-click the Install Linux Mint icon in the Desktop. Welcome windows will pop up. Just click Continue to start the installation.
On the ‘Installation type’ step above, choose ‘Something else’. We will install Linux Mint on the partition we have created on the above step. Then click Continue.
As you can see in the image above, select the partition then click Change to edit the partition. Format it as EXT4 file system and mount it as ‘/’. Click OK and then click Install Now. You may be warned that there is no SWAP space configured at the moment. Just ignore it. We can create swap space later.
Follow the on screen installation step. Once the installation complete, DO NOT reboot it now. Click Continue Testing. We need to install EFI boot manager, a tool used to modify the Intel Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) Boot Manager.
Open Terminal program then run the following command to install EFI boot manager.
Then run ‘sudo efibootmgr’ to see current boot status. See the image below for example.
As you can see above, BootCurrent is 0000 which is Ubuntu (Linux Mint is based on Ubuntu). BootOrder is 0000,0080 which means Ubuntu first then Mac OS X. To make sure the boot order is correct, run the following command:
You can now restart the Linux Mint Live USB. You should see Grub boot menu with Linux Mint in the first order.
Post-install configuration
Setting the Grub menu
Linux Install For Mac
As you can see in the Grub menu above, the Grub automatically probes and detects other operating systems installed in other partitions. It detects Mac OS X (32 and 64 bit) on /dev/sdb4. Unfortunately when we select it, it does not boot into the system. We need to manually add a menu entry of the OS in /etc/grub.d/40_custom file as follow for example:
As both menuenty of Mac OS X (32-bit) / (64-bit) (on /dev/sdb4) do not work, we need to remove it by disabling the Grub probe option. It can be done by simply make the file /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober not executable.
Linux Installer For Mac Download
Then re-run the update-grub
Restart to see the new Grub menu as follows:
Install Wireless / WiFi driver
The wireless is not detected by default. We need to install the wireless kernel driver as follows:
Installer Linux Macbook
Macbook Pro is using Broadcom BCMxx for the wireless firmware so we need to install it as above.
